Effective Strategies for Wheat Weevil Control

Wheat weevil control is an essential aspect of maintaining the quality and yield of wheat crops. These small pests can cause significant damage if left unchecked, leading to financial loss and impacting the overall efficiency of farming operations. Understanding how to manage and eliminate these pests is crucial for farmers and agricultural businesses alike.
What are Wheat Weevils?
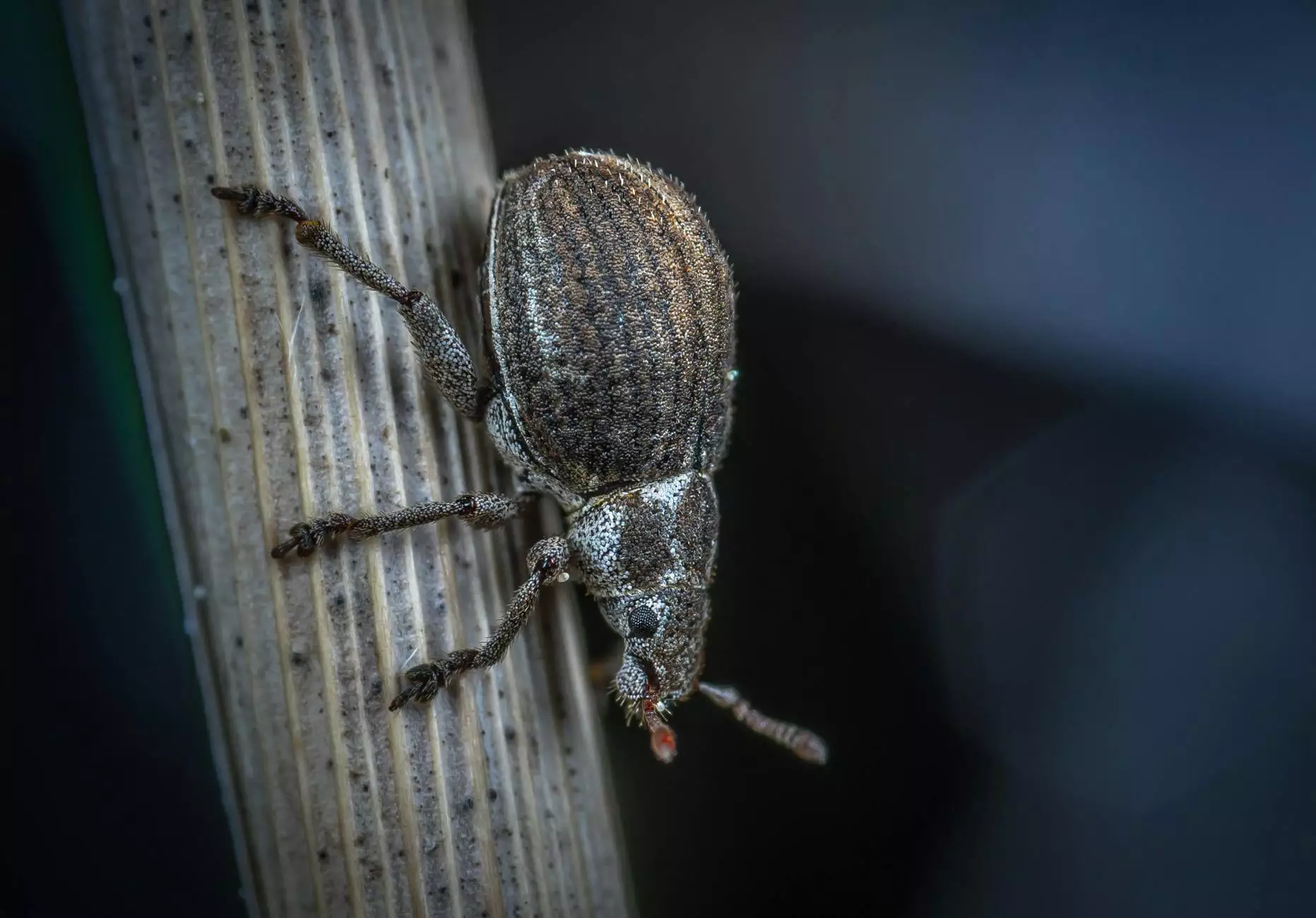
The wheat weevil (*Sitophilus granarius*) is a small insect that primarily infests stored grains, particularly wheat. They are characterized by their elongated bodies and distinctive snouts. Adult weevils measure about 2-5mm in length, and their larvae cause the most damage by feeding on the grain within the kernels. This can lead to a decrease in grain quality and can even render it unsuitable for sale or consumption.
Understanding the Life Cycle of Wheat Weevils
To effectively implement wheat weevil control, it is essential to understand their life cycle:
- Egg Stage: Female weevils lay eggs inside the grain kernels. Each female can lay up to 400 eggs.
- Larvae Stage: The eggs hatch into larvae within a few days, feeding on the grain as they develop.
- Pupal Stage: After 2-4 weeks, larvae pupate within the kernels.
- Adult Stage: Adults emerge, ready to mate and repeat the cycle.
Each life cycle can take as little as 4 weeks under optimal conditions, making rapid response critical in wheat weevil control strategies.
Signs of Wheat Weevil Infestation
Being proactive is vital when it comes to wheat weevil control. Here are some signs that may indicate an infestation:
- Presence of Adult Weevils: Finding adults crawling in or near grain storage is a clear indicator.
- Holes in Grain: Small exit holes in wheat kernels are a sign that larvae have already infested them.
- Dust and Frass: Accumulation of powdery dust or frass (insect waste) around storage areas indicates activity.
- Environmental Factors: Warm, humid conditions can foster weevil populations, so monitor your storage environment closely.
Preventative Measures for Wheat Weevil Control
Preventing infestations is the first line of defense in wheat weevil control. Here are some effective preventative measures you can implement:
1. Proper Grain Storage
Ensure that your grain is stored in a clean, dry, and airtight environment. Seal all storage containers and regularly check for any leaks or damage.
2. Regular Inspections
Conduct frequent inspections of stored grain. Look for any signs of infestation and take immediate action if detected.
3. Temperature Control
Maintaining cooler temperatures can significantly inhibit weevil reproduction. Consider cooling systems or regularly ventilating storage areas.
Effective Control Methods for Established Infestations
If an infestation is confirmed, you can implement several effective control methods:
1. Chemical Treatments
Insecticides can be employed to manage wheat weevil populations effectively. It is crucial to use products that are labeled specifically for weevils and to follow all safety guidelines. Some widely used chemicals include:
- Boric Acid: An effective choice for managing stored product pests.
- Pyrethroids: These are synthetic chemicals that target adult weevils and larvae.
- Fumigants: Fumigation can eradicate pests within the storage environment. Ensure all procedures comply with local regulations.
2. Biological Control
Utilizing natural predators, such as certain parasitic wasps, can help control wheat weevil populations. Integrating biological controls can be a sustainable and effective long-term strategy.
3. Physical Controls
Implementing physical barriers, such as traps or nets, can help reduce weevil access to grains. Regular cleaning and removal of spilled grains can significantly lower the risk of infestations.
Best Practices for Ongoing Wheat Weevil Control
After controlling an infestation, it is vital to establish ongoing practices to prevent future problems:
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of infestations, treatments, and monitoring activities.
- Training and Education: Invest in training for staff involved in grain storage and management to recognize early signs of infestation.
- Collaboration: Work with local agricultural extension services or pest management professionals for ongoing support and resources.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Approach to Wheat Weevil Control
In conclusion, effective wheat weevil control requires a thorough understanding of the pest's biology, preventive measures, active management strategies, and ongoing monitoring. By incorporating these practices into your farming operations, you can help ensure the health of your wheat crops and protect against financial loss due to infestations.
For additional resources or to learn about our farming equipment solutions, visit TSGC Inc. today. Together, we can safeguard your agricultural ventures from the threats posed by pests like the wheat weevil.